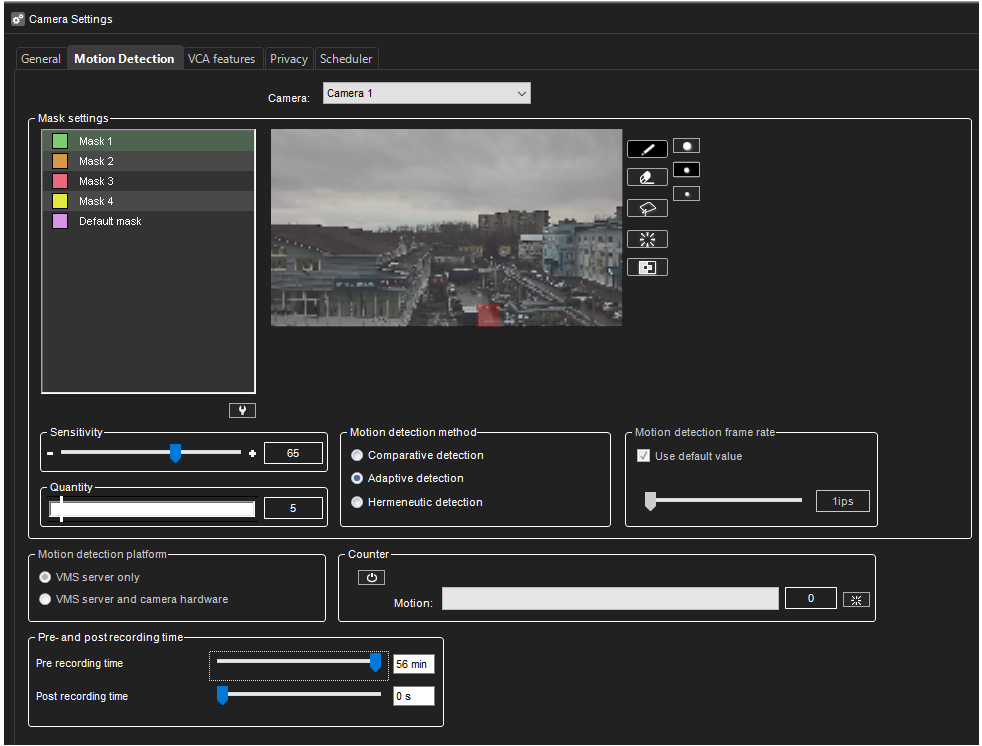
Sensitivity and quantity
The system detects motion when:
-
Pixels change more than the set limit (Sensitivity).
-
The specified number of pixels change (Quantity).
If there is a lot of background noise in the image, for example, changes in lighting conditions, decrease the sensitivity by dragging the slider to the left or increase the quantity limit by dragging the slider to the right.
Motion detection methods
Comparative detection
Compares an image to the image before it. If the differences exceed the set limits, the system detects motion.
You can use comparative motion detection in most conditions.
However, if there is a lot of movement in the background, for example, rain, moving leaves, or changes in light levels, use adaptive motion detection.
Adaptive detection
Compares each image to a background image. The system learns the background image and the movement that belongs there automatically.
Thus, the system does not interpret, for example, moving leaves as motion.
In addition, if more than half of the pixels in an image change, the system concludes that the lighting conditions have changed.
As a result, it resets the reference image and starts learning it again.
Hermeneutic detection
Is a sophisticated motion detection system for challenging weather conditions (e.g. heavy rain, “noisy” background image, etc.) and situations in which external video content analytics (VCA) tools are used.
It should be noted that hermeneutic detection requires more processing resources than the other detection methods.
Motion detection frame rate
Defines the frame rate used in motion detection.
It is generally recommended to use the default frame rate.
For IP cameras, motion detection uses intra-frames and matches the intra-frame rate.
Typically, this is one image per second.
Counter
-
Enable Counter
-
Check the motion values
-
The camera image shows which area of the camera image causes motion detection recording
