Hardening VMS Components
Components to protect
Servers (physical and virtual)
Network
Software applications
Cameras
Configure the VMS with roles that control access to the system, and designate tasks and responsibilities. (AC2, AC3, AC6, AC16, AC25, AU6, AU9, CM5, CM11, IA5, PL8, PS5, PS7, SC2, SI7, in Appendices D and F in NIST SP 800-53 Rev4).
Hardening servers (physical and virtual)
Overview
Server hardening is a general system hardening process that involves securing a server's data, ports, components, functions, and permissions using advanced security measures at the hardware, firmware, and software layers.
These general server security measures include, but are not limited to:
Keeping a server’s operating system patched and updated
Regularly updating third-party software essential to the operation of the server
and removing third-party software that doesn’t conform to established
cybersecurity standards
Using strong and more complex passwords and developing a strong password
policies for users. (See password policy in Appendices)
Locking user accounts if a certain number of failed login attempts are registered
and removing needless accounts
Disabling USB ports at boot
Implementing multi-factor authentication
Using self-encrypting drives or AES encryption to conceal and protect sensitive
information
Using firmware resilience technology, memory encryption, antivirus and firewall
protection, and advanced cybersecurity suites specific to your operating system, such as Titanium Linux
Restrict access to servers. Keep servers in locked rooms, and make it difficult for intruders to access network and power cables. (PE2 and PE3 in Appendices D and F in NIST SP 800-53 Rev4 (http://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/specialpublications/nist.sp.800-53r4.pdf) (PE Physical and Environment Protection).)
Mirasys VMS servers
1) Use physical access controls and monitor the server room
Mirasys recommends placing the hardware with the servers installed in a designated server room and using physical access controls. In addition, you should maintain access logs to document who has had physical access to the servers. Surveillance of the server room is also a preventive precaution.
Mirasys supports the integration of access control systems and their information. For example, you can view access logs in Mirasys Spotter.
2) Use encrypted communication channels
Mirasys recommends that you use a VPN for communication channels for installations where servers are distributed across untrusted networks. This is to prevent attackers from intercepting communications between the servers. Even for trusted networks, Mirasys recommends using HTTPS to configure cameras and other system components.
3) Run services with service accounts
Mirasys recommends that you create service accounts for services related to Mirasys VMS instead of using a regular user account.
Set up the service accounts as domain users and only give them the permissions required to run the relevant services. See Kerberos authentication (explained). For example, the service account should not be able to log on to the Windows desktop.
5) Run components on dedicated virtual or physical servers
Mirasys recommends that you run the components of Mirasys VMS only on dedicated virtual or physical servers without any other software or services installed.
6) Restrict the use of removable media on computers and servers
Mirasys recommends that you restrict the use of removable media, for example, USB keys, SD cards, and smartphones, on computers and servers where components of Mirasys VMS are installed.
This helps prevent malware from entering the network. For example, allow only authorized users to connect removable media when you need to transfer video evidence.
7) Use individual administrator accounts for better auditing
Mirasys recommends using individual accounts for administrators instead of shared administrator accounts. This lets you track who does what in Mirasys VMS to help prevent malware from entering the network. You can then use an authoritative directory such as Active Directory to manage the administrator accounts. You assign administrator accounts to roles in System Manager\User group\System Manager Enterprise role
8) Use subnets or VLANs to limit server access
Mirasys recommends that you logically group different types of hosts and users into separate subnets.
This can have benefits in managing privileges for these hosts and users as members of a group with a given function or role.
Design the network so that there is a subnet or VLAN for each function. For example, one subnet or VLAN for surveillance operators and one for administrators. This allows you to define firewall rules by group instead of individual hosts.
Management Server
Enable only the ports used by the management server. Documenting and maintaining security settings on each system.
Mirasys recommends enabling only the ports used by the management server and blocking all other ports, including the default Windows ports. This guidance is consistent for the server components of Mirasys VMS.
The management server ports used in Mirasys VMS are:
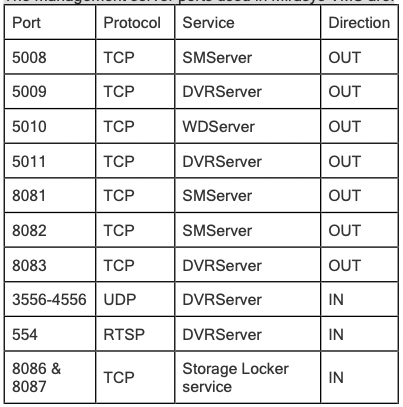
The ports used depend on the deployment. If in doubt, contact Mirasys Support.
Recording Server
Use separate network interface cards.
Mirasys recommends using multiple network interface cards (NICs) to separate the communication between recording servers and devices from between recording servers and client programs. Client programs do not need to communicate directly with devices, with the exception of TruCast, for which Spotter Client needs direct access to devices.
Hardening the network
Network Infrastructure
Network hardening involves securing the basic communication infrastructure of multiple servers and computer systems operating within a given network.
Two main ways network hardening is achieved are through establishing an intrusion prevention or intrusion detection system, which are usually software-based.
These applications automatically monitor and report suspicious activity in a given network and help administrators prevent unauthorized access to the network.
Network hardening techniques include properly configuring and securing network firewalls, auditing network rules and network access privileges, disabling certain network protocols and unused or unnecessary network ports, encrypting network traffic, and disabling network services and devices not currently in use or never in use.
Network hardening
If left unprotected, cameras and their network connections represent a significant risk of compromise, potentially giving intruders further access to the system.
1) Use secure and trusted networks connection.
Mirasys recommends selecting cameras that support HTTPS. Network communications must be secure, whether or not you are on a closed network. By default, secure communications should be used when accessing the VMS. For example:
VPN tunnels or HTTPS by default
The latest version of the Transport Layer Security
(https://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/tls/charter/ ) (TLS, currently 1.2) with valid certificates that meet industry best practices, such as from Public-Key Infrastructure (X.509) (https://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/ipsec/documents/ ) and CA/Browser Forum (https://cabforum.org/ ).
Otherwise, credentials may be compromised and intruders might use them to access the VMS.
Configure the network to allow client computers to establish secure HTTPS sessions or VPN tunnels between the client devices and the VMS servers.
2) Use firewalls to limit access to servers and computers
Mirasys recommends that you use secure connections and the following additional steps:
Use secure device authentication
Use TLS
Use device whitelisting to authenticate devices
Use firewalls to limit network communication between servers and client
computers and programs.
All Mirasys VMS components and the ports needed by them are listed in individual sections below.
To ensure, for example, that the firewall blocks only unwanted traffic, you need to specify the ports that the Mirasys VMS uses.You should only enable these ports.
The lists also include the ports used for local processes.
3) Use a firewall between the VMS and the Internet
The VMS should not connect directly to the Internet.
If you expose parts of the VMS to the Internet, Mirasys recommends that you use an appropriately configured firewall between the VMS and the Internet.
If possible, expose only the Mirasys Gateway component to the Internet, and locate it in a demilitarized zone (DMZ) with firewalls on both sides.
4) Connect the camera subnet to the recording server subnet only
Mirasys recommends that you connect the camera subnet only to the recording server subnet.
The cameras and other devices need to communicate only with the recording servers, with the exception of when TruCast is used by Spotter.
5) Use secure wireless protocols
If you use wireless networks, Mirasys recommends that you use a secure wireless protocol to prevent unauthorized access to devices and computers. For example, use standardized configurations.
The NIST guidance on wireless local area networks provides specific network management and configuration details.
For more information, see SP 800-48 revision 1, Guide to Securing Legacy IEEE 802.11 Wireless Networks (Guide to Securing Legacy IEEE 802.11 Wireless Networks).
Additionally, Mirasys recommends not using wireless cameras in mission-critical locations. Wireless cameras are easy to jam, leading to video loss.
6) Use port-based access control
Use port-based access control to prevent unauthorized access to the camera network. The port should become blocked if an unauthorized device connects to a switch or router port. Information about how to configure switches and routers is available from the manufacturers.
Please see SP 800-128 ( Guide for Security-Focused Configuration Management of Information Systems) for information about configuration management of information systems.
7) Run the VMS on a dedicated network
Mirasys recommends that, whenever possible, you separate the network where the VMS is running from networks with other purposes.
For example, a shared network such as the printer network should be isolated from the VMS network.
In addition, Mirasys VMS deployments should follow a general set of best practices for system interconnections.
8) Restrict unused services and protocols
To help avoid unauthorized access or information disclosure, Mirasys recommends that you stop unused services and protocols on devices.
For example, Telnet, SSH, FTP, UPnP, and Ipv6.
If UPnP is disabled, then the camera discovery will not work for all cameras.
Using strong authentication on any services that access the VMS, network, or devices is also important.
For example, use SSH keys instead of user names and passwords and certificates from a Certificate Authority for HTTPS.
For more information, see the device manufacturer's hardening guides and other guidance.
9) Other recommendations
It is recommended that Mirasys Spotter is on the same VLAN as the servers.
Use a VPN-encrypted network or similar if using Mirasys Spotter from a remote
location.
Mirasys recommends that customers use data encryption between the VMS server
and clients
Software application hardening
All software applications
Software application hardening, or just application hardening, involves updating or implementing additional security measures to protect both standard and third-party applications installed on your server.
Unlike server hardening, which focuses more broadly on securing the entire server system by design, application hardening focuses on the server’s applications, specifically including, for example, a spreadsheet program, a web browser, or a custom software application used for a variety of reasons.
At a basic level, application hardening involves updating existing or implementing new application code to secure a server further and implementing additional software-based security measures.
Examples of application hardening include, but are not limited to:
Patching standard and third-party applications automatically
Using firewalls
Using antivirus, malware, and spyware protection applications
Using software-based data encryption
Using CPUs that support Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX)
Using an application like LastPass to manage and encrypt passwords for
improved password storage, organization, and safekeeping
Establishing an intrusion prevention system (IPS) or intrusion detection system
(IDS)
Client programs
The sections below provide guidance about how to protect the Mirasys client programs. The client programs are:
Mirasys System Manager
Mirasys Web Client
Mirasys Spotter
Spotter Mobile
Always run clients on trusted hardware on trusted networks
Mirasys recommends that you always run Mirasys clients on hardware devices with the proper security settings.
Specific guidance for mobile devices is available in SP 800-124 (SP 800-124).
These settings are specific to the device.
Hardening cameras
It is recommended to set the cameras on separate VLANs and use HTTPS for the camera to Recording Server communication.
Mirasys Spotter
1) Restrict physical access to any computer running Mirasys Spotter
Mirasys recommends that you restrict physical access to computers running Mirasys Spotter.
Allow only authorized personnel to access the computers.
For example, keep the door locked, and use access controls and surveillance.
2) Always use a secure connection by default, particularly over public networks
If you need to access the VMS with Mirasys Spotter over a public or untrusted network, Mirasys recommends using a secure VPN connection. This helps protect communication between Mirasys Spotter and the VMS server.
3) Enable a Second password in use
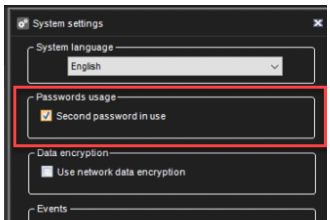
4) Create a customer Mirasys Spotter Enterprise role
Turn on only required features, and turn off features that a surveillance operator does not need. The point is to limit opportunities for misuse or mistakes.
5) Use separate names for user accounts
Mirasys recommends creating a user account for each user and using a naming convention that makes it easy to identify them personally, such as their name or initials. This is a best practice for limiting access to only what is necessary and reducing confusion when auditing.
6) Prohibit the use of removable media
For video exports, establish a chain of procedures that are specific to evidence. Mirasys recommends that the security policy allows only authorized Mirasys Spotter operators to connect removable storage devices such as USB flash drives, SD cards, and smartphones to the computer where Mirasys Spotter is installed.
Removable media can transfer malware to the network and subject video to unauthorized distribution.
Alternatively, the security policy can specify that users can export evidence only to a specific location on the network or to a media burner only. You can control this through the Mirasys Spotter Enterprise Plus role.
4. System Manager
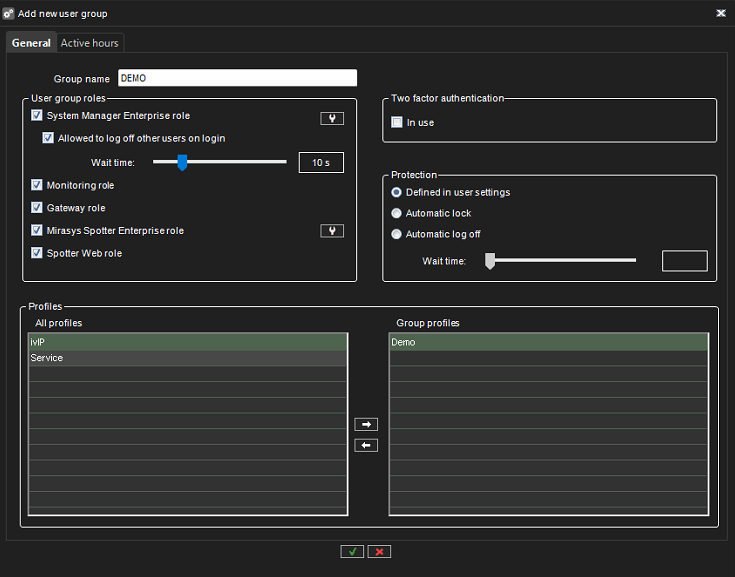
1) Allow administrators to access relevant parts of the VMS
If a setup requires multiple administrators, Mirasys recommends configuring different administrator rights for administrators who use the System Manager.
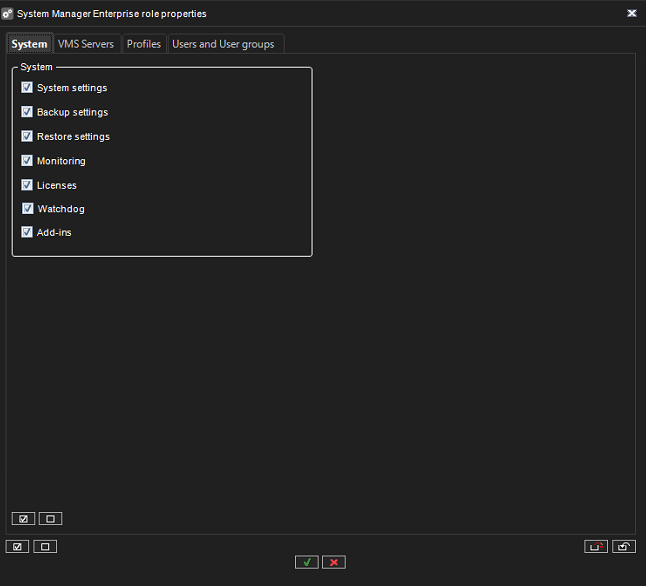
2) Run the System Manager on trusted and secure networks
If you access the System Manager over HTTP, the plain text communication can contain unencrypted system details. Mirasys recommends that you run the System Manager only on trusted and known networks.
Use a VPN to provide remote access.
Physical security considerations
Use of physical barriers to servers and client computers
Camera enclosures, locks, tamper alarms, and access controls
